
La Cámara de Santiago del Estero se incorporó a FAIMA
FAIMA está integrada actualmente por 28 cámaras en todo el país
La Cámara de la Industria de la Madera de Santiago del Estero, recientemente incorporada a la Federación, participó por primera vez de la reunión de Comisión Directiva. En esta oportunidad, asistieron el Lic. Vicente Spitale, Presidente; Gustavo Diambra, Vicepresidente y la Ing. Graciela Hoyos, Asesora de la entidad.
En este encuentro, los directivos de las distintas cámaras que integran la Federación se presentaron y les dieron la bienvenida. Leandro Mora Alfonsín, Director Ejecutivo de FAIMA, les informó qué servicios ofrece FAIMA, la dinámica de trabajo de las subcomisiones y de la Comisión Directiva. Por su parte, los representantes de la Cámara de Santiago comentaron en qué temas están trabajando actualmente.
De esta forma, FAIMA está integrada actualmente por 28 cámaras en todo el país, siendo la única entidad de 2º grado que representa a nivel nacional al sector industrial maderero.

IT MAY INTEREST YOU
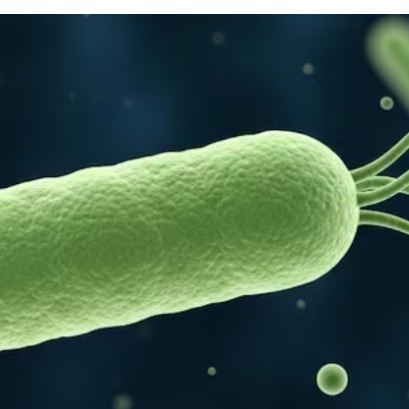 The discovery of methane-producing bacteria in trees rethinks the ecological role of forests
The discovery of methane-producing bacteria in trees rethinks the ecological role of forests
Pioneering study shows trees surprising internal microbial diversity and potential influence on global climate, driving novel strategies for agricultural and forestry management
 Nation reinforces prevention and training against forest fires
Nation reinforces prevention and training against forest fires
The director of the Federal Emergency Agency (AFE), Santiago Hardie, referred to the support that the Nation provides in fighting fires. He argued that the majority of igneous sources respond to human interventions and that, therefore, social awareness is a central tool to reduce environmental, material and human damage.
 The South American country that changes construction thanks to an ancient, mega-resistant material: more than steel
The South American country that changes construction thanks to an ancient, mega-resistant material: more than steel
This material that grows in South America creates the most resistant constructions and radically changes the world of architecture One particular building material has been used for millennia by various cultures in South America. This is due to its structural resistance that allows the creation of homes, bridges and shelters. Its archaeological presence shows that it was one of the most valued construction resources in seismic and humid areas.





















